Label Based High Density Arrays
Label Based Antibody Arrays
Semi-quantitative, Label Based, High Density Antibody Arrays
With label based high density array platforms, researchers can now detect up to 2000 proteins simultaneously, obtaining a broad, panoramic view of protein expression. The newly expanded panels include a wide variety of metabolic enzymes, structural proteins, epigenetic markers, neuroregulatory factors, in addition to very popular lists of cytokines, growth factors, receptors, adipokines, proteases, and signaling proteins.
Available on both glass slide and membrane formats, this array type is ideally suited for biomarker discovery studies and exploratory screens.
Research Applications
- High throughput expression & phosphorylation profiling
- Discovering potential molecular targets for drug development
- Uncovering molecular mechanisms of drug action
- Identifying crucial factors involved in disease processes
- Discovering biomarkers for disease management
- Discovering expression & phosphorylation patterns for molecular classification of diseases
Features
- High detection sensitivity
- Easy to use; obtain results in 2 days
- No need for fractionation, depletion or extraction of samples
- Consumes only 20-30 ul of serum/plasma
- No dedicated equipment needed (membrane arrays)
- Scanning services available for glass slides
- Accurate and reproducible
- Very reasonable costs per target
How It Works
Through a simple labeling process, the sample proteins are directly conjugated to biotin, eliminating the need for a second antibody to develop the array signals. In this format, unintended antibody interactions are impossible, thus eliminating limitations on the size of the array panel.
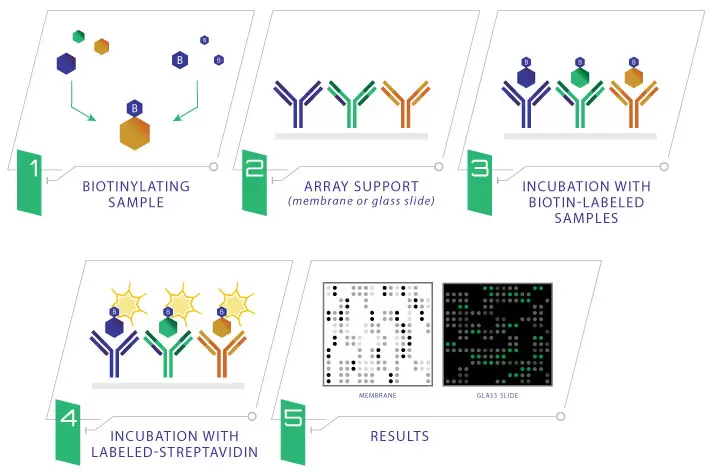 Label-Based Arrays differ from traditional sandwich ELISA-based arrays primarily in the means of detection. Instead of using a second biotinylated antigen-specific antibody, sample proteins themselves are labeled with biotin prior to incubation with the capture antibodies. Proteins binding to the array can be detected using streptavidin-HRP for chemiluminescence detection or streptavidin-conjugated fluor for fluorescence detection.
Label-Based Arrays differ from traditional sandwich ELISA-based arrays primarily in the means of detection. Instead of using a second biotinylated antigen-specific antibody, sample proteins themselves are labeled with biotin prior to incubation with the capture antibodies. Proteins binding to the array can be detected using streptavidin-HRP for chemiluminescence detection or streptavidin-conjugated fluor for fluorescence detection.