Exosome Engineering
Exosome Engineering
Deliver specific proteins and microRNAs to target cells
Used by cells to transport cargoes of active biomolecules, exosomes are emerging as a powerful way for scientists to deliver specific proteins and miRNAs to target cells. As the field transitions from observation and analysis of exosomes to custom exosome design for therapeutics and other uses, BioCat is already offering the necessary tools to push exosome engineering to the next level.
XPack™ Exosome Protein Engineering
- Package reporter proteins into secreted exosomes to track cargo delivery
- Express and package any protein to create biotherapeutic exosomes
- Generate bioluminescent exosomes for tracking delivery in vivo
- Create stable cell lines producing XPack exosomes with any protein cargo
The natural function of exosomes as cell to cell communication vehicles makes them attractive for use as therapeutic shuttles to deliver biological molecules or drugs to target disease cells. Our partner SBI has identified a specific peptide sequence that targets a protein to the interior exosomal membrane, allowing them to be packaged into exosomes for secretion. This “XPack” peptide sequence has been incorporated into the XPack cloning and expression lentivectors, allowing for reporter proteins or any protein of interest to be loaded into exosomes within a producer cell line, then delivered to target cells of choice. Additionally, stable XPack cell lines have been generated that serve as a constant source of exosomes loaded with reporter protein cargo (GFP or luciferase), enabling tracking of exosome dynamics in both human cells and in vivo murine models. Purified, ready-to-use exosomes from these stable cell lines are also available as part of the comprehensive XPack system.
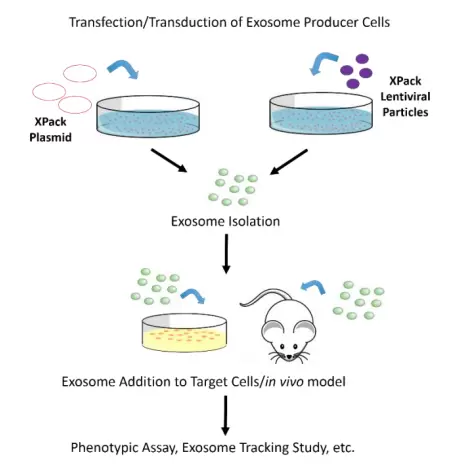
XMIR™ Exosome RNA Packaging
The exosomal RNA content varies, depending upon the cell from which the exosomes was secreted. The mechanism of how specific RNA sequences are selectively packaged into exosomes is an intensive area of investigation. Our partner SBI has evaluated numerous exosome NGS data sets and has identified a specific RNA sequence tag that targets a small RNA to be packaged into exosomes for secretion. The “XMotif” RNA sequence tag has been incorporated into the miRNA and antimiRNA oligos for the XMIR and AXMIR products and has been built into the XMIRXpress cloning and expression lentivectors, enabling packaging of specific sense or antisense miRNAs into exosomes. Simply transfect one of our XMotif-tagged miRNAs or lentivectors into the exosome-producing cells of your choice. The secreted exosomes will be enriched for your miRNA, which can then be delivered to target cells. Great for knocking down or upregulating expression of a target in the recipient cells.
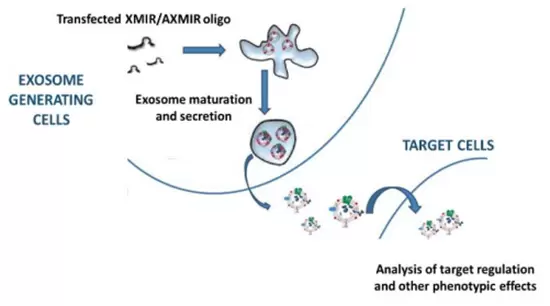
XStamp™ Exosome Targeting
- Display proteins on the surfaces of secreted exosomes
- Coat exosomes with targeting ligands
- Target engineered exosomes to specific cellular destinations
- Create stable cell lines producing XStamp exosomes with any display protein for targeting
The exosome surface display system developed by our partner SBI enables desired protein sequences to be placed efficiently on the surfaces of engineered exosomes called the "XStamp" technology. The XStamp technology is based upon a C-terminal fusion of ligands that results in the efficient display of the ligands on the surfaces of secreted exosomes. The C1C2 fusion domain is derived from the human MFG-E8 protein and has been shown to be abundant and nearly exclusively localized on the surfaces of exosomes. This C1C2 domain is what is termed the “XStamp” tag. Protein sequences that are fused to the XStamp tag will efficiently display the protein ligand fusion on the surfaces of secreted exosomes. The technology can be used to place cellular “addresses” on exosomes that send them to specific destinations for cargo delivery.
In addition to the XStamp Cloning and Expression Lentivector for creating target-specific extracellular vesicles of your interest, ready-to-use lentivectors with a given XStamp, e.g. NCAM-XStamp, are offered.
MFG-E8 Localizes to Exosome Surfaces (C1C2 domain)
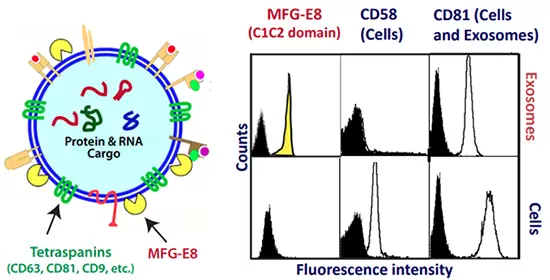
Fluorescently-labeled antibodies for MFG-E8, CD58 and CD81 were used in combination for FACs analysis. The CD58 marker is a known cell surface marker that is absent on exosomes. CD81 is known to be present both in cells and exosomes. The FACs data show that MFG-E8 is exclusively detected on exosomes and not present in the cells.
XStamp Expression Lentivector
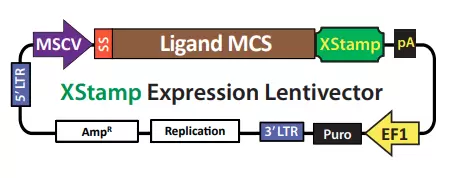
To take advantage of the localization of MFG-E8 on exosomes, the C1C2 domain (XStamp domain) of the protein’s gene was cloned into SBI’s MSCV-MCS-EF1-Puro lentivector and a 5’ secretion signal sequence (SS) was placed within the multiple cloning site. The protein ligand chosen to display on exosomes is cloned into the MCS and fused to the C1C2 domain.